Description of Airport Generalization Algorithms
- Date 20/07/2017.
- Author: Guillaume Touya
- Contact {firstname.lastname}@ign.fr.
Description of the algorithm
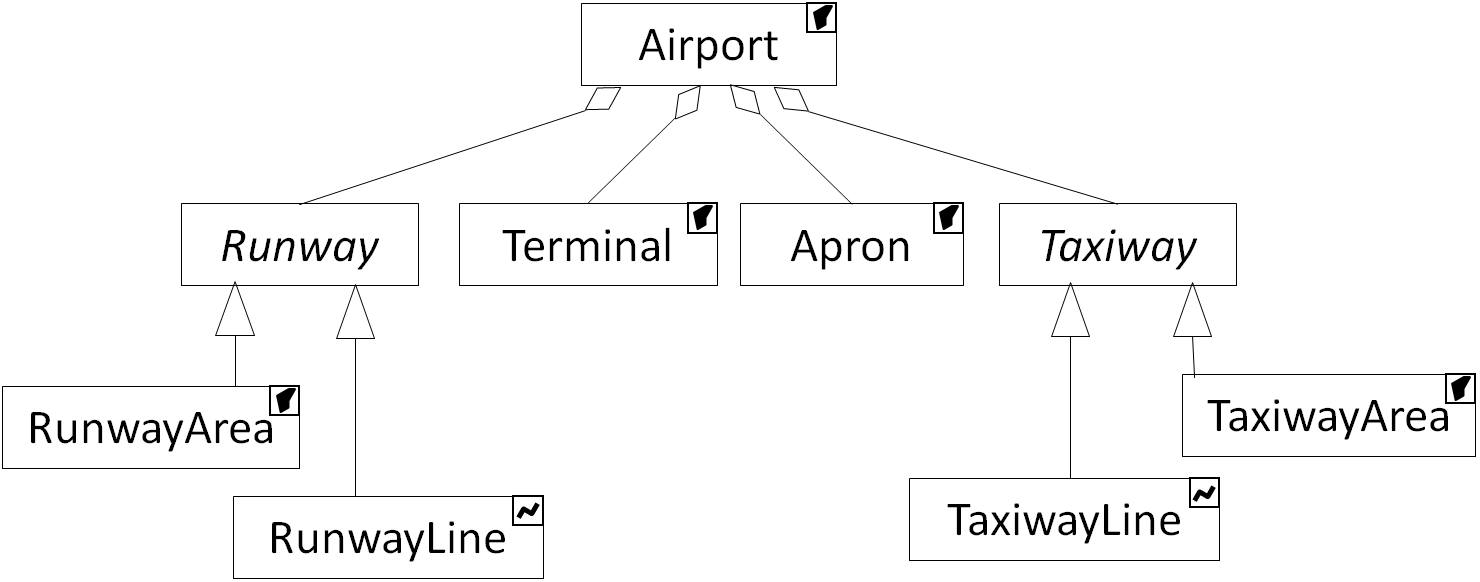
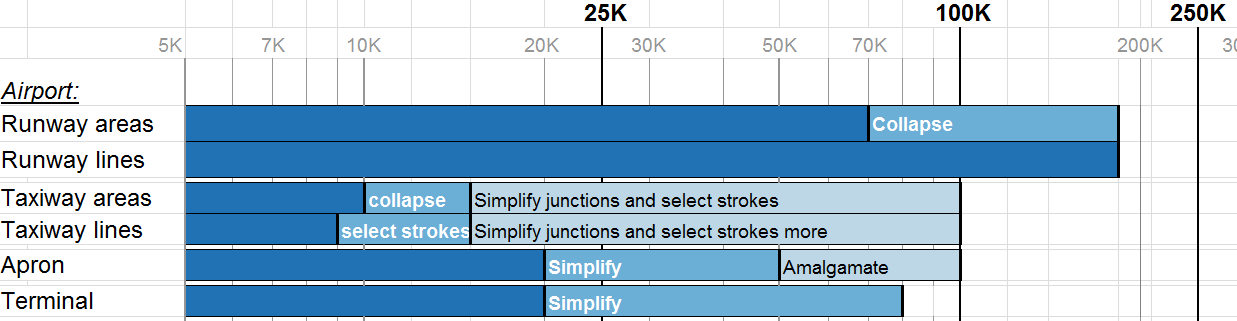
Airports are complex objects composed of several geographical features such as runways, taxiways, aprons, or terminals (see UML diagram below). They all have to be generalized and CartAGen contains several algorithms dedicated to this complex feature.

The paper that describes these algorithms can be found here
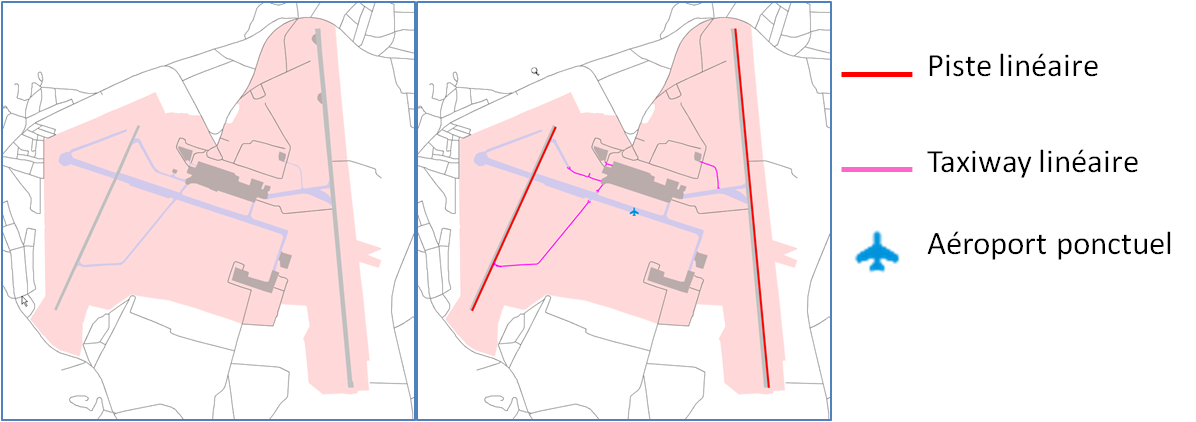
Runway collapse
The polygon to line collapse algorithm used for runways is much simpler than the skeletonize algorithm. First, we compute the global orientation of the runway using the Minimum Bounding Rectangle (see Duchêne et al. 2003). Then, we search for the longest segment that can be built inside the runway polygon with the orientation of the runway, and this segment replaces the runway polygon.
| Parameter name | Description | Type | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
| fusion | if true, the runway polygons that touch are merged before collapse | boolean | true |
| collapse | if true, the runway polygons are collapsed into lines | boolean | true |
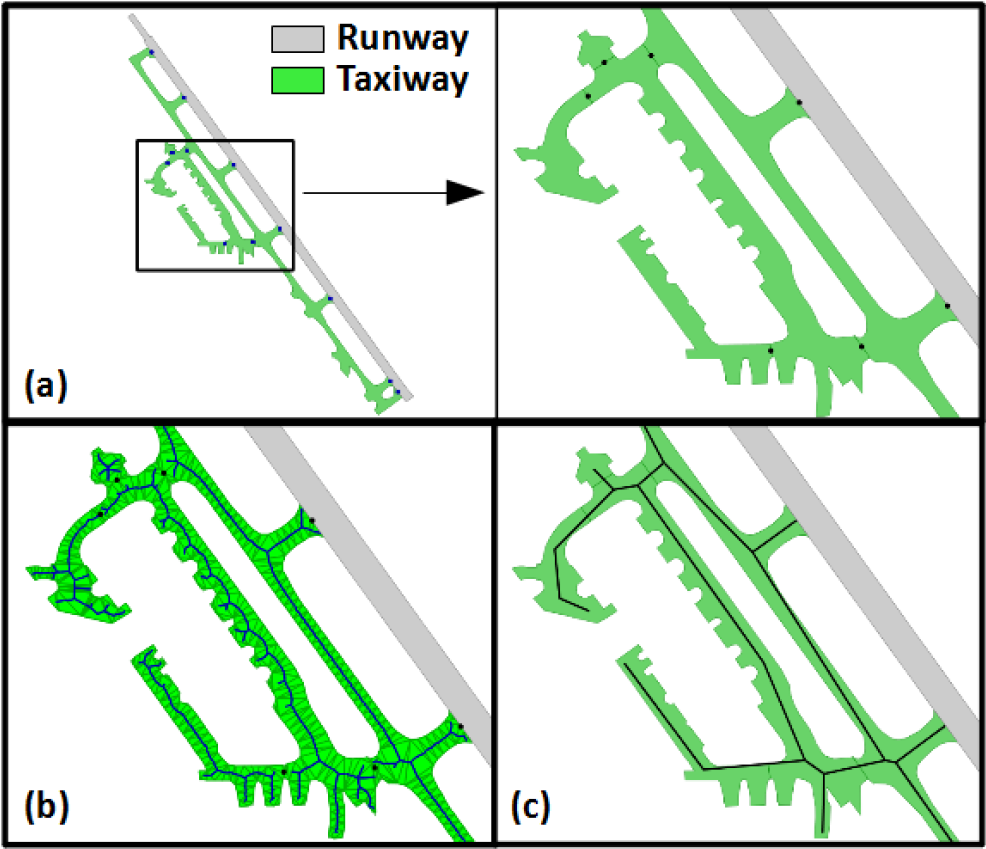
Taxiway collapse
The taxiway collapse algorithm combines morphological operators to identify thin parts of the taxiway polygons that should be collapsed, and then removes these parts from the initial polygon. The removed thin parts are then skeletonized.
| Parameter name | Description | Type | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
| openThreshTaxi | the width threshold for deciding if parts of a taxiway should be collapsed into a line | double (m) |
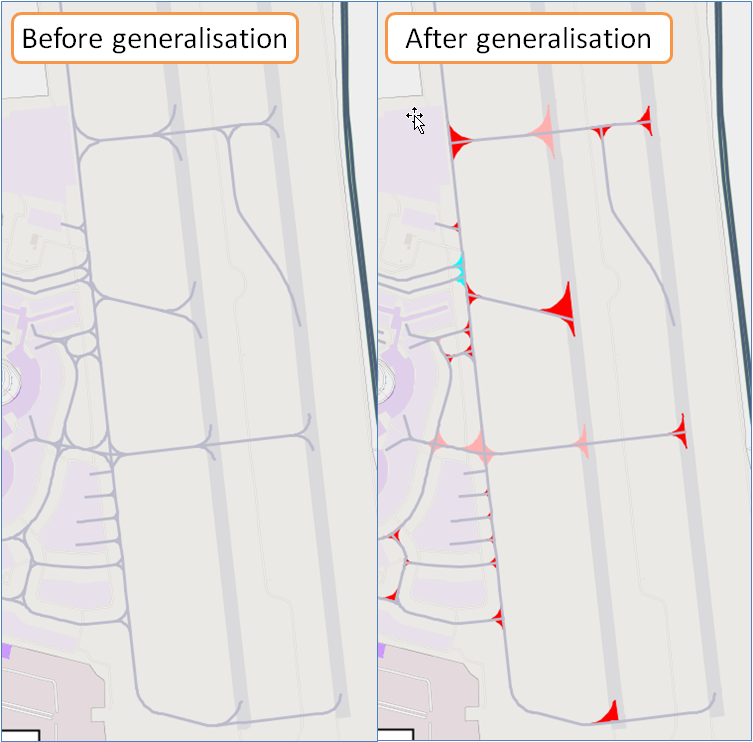
Taxiway typification
Taxiway typification only processes taxiway lines. It identifies the complex junctions in the taxiway network and typifies them into simple junctions. When junctions have been typified, strokes are computed into the remaining lines, and only the longest strokes are kept, while the small ones are removed.
| Parameter name | Description | Type | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
| branchingMaxArea | the maximum area for a face of the taxiway graph to be considered as a possible complex junction | double (m²) | 7000.0 |
| maxAngleBranching | the maximum angle value to be considered as sharp in the complex junction typification process | double (radians) | 1.5 |
| taxiwayLengthThreshold | the minimum length for a taxiway stroke to be kept in the map | double (m) |
Other operators
Simple algorithms are also available to:
- amalgamate apron polygons that are touching or close to each other into a single bigger polygon,
- to simplify apron polygons,
- to simplify terminal polygons.
Examples of generalization
When to use the algorithm?
These algorithms have been successfully applied to OpenStreetMap airports from all over the world, and to authoritative datasets.