Description of the Building Aggregation Algorithm by N. Regnauld
- Date 20/07/2017.
- Author: Guillaume Touya
- Contact {firstname.lastname}@ign.fr.
Description of the algorithm
This algorithm aggregates two close buildings by determining the joining polygon that makes the most compact shape.
The image below shows how edges of each polygon are extended to straight lines and the intersections between these straight lines are used to create different possible aggregated polygons. In the case below, the polygon b) is preferred by the algorithm.
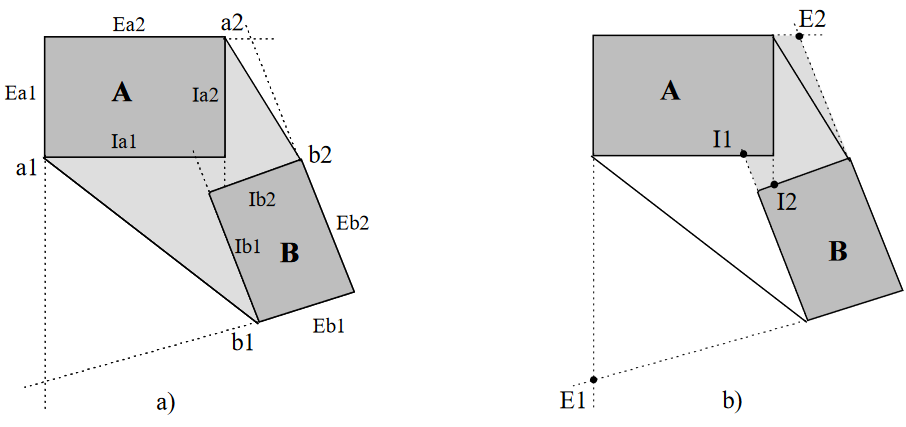
See more details about the algorithm in N. Regnauld’s PhD (in French).
Examples of generalization
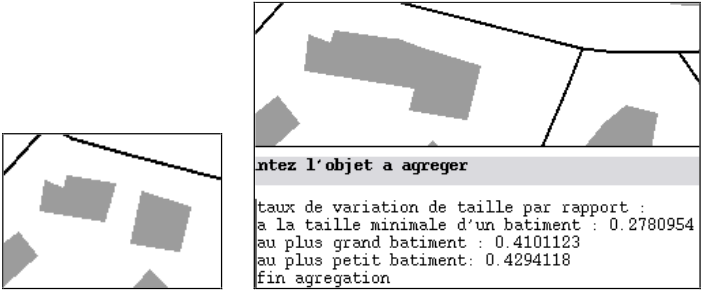
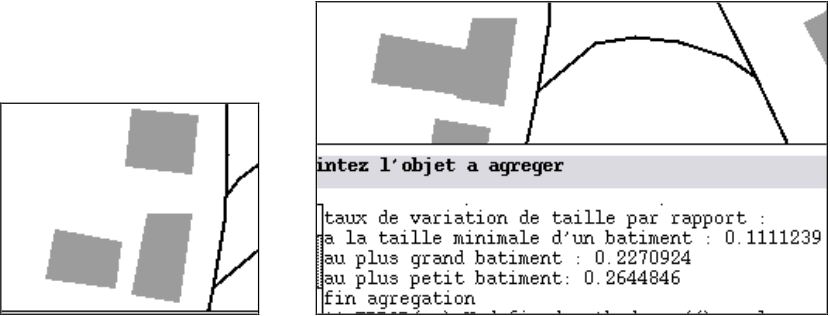
When to use the algorithm?
This algorithm was initially developed for the aggregation of two close buildings. It can be extended to other man-made polygon features, what C. Duchêne calls small compact features, e.g. sports fields, greenhouses or similar map features.